Totomycin
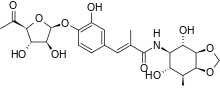
Totomycin (also known as hygromycin A) is an aminoglycoside antibiotic produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus, first described in the 1950s. The bacteria source is similar to that of hygromycin B from which the name of the compound was derived.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Hygromycin A, Homomycin |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H29NO12 |
| Molar mass | 511.480 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 110 to 112 °C (230 to 234 °F) (decomp.) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
History
Hygromycin A was discovered in a soil sample from a forest near Indianapolis, Indiana in 1953 by Waksman and Henrici.[1] Identification and structure of totomycin wasn't determined until 1957.
Antibiotic activity
The strongest antibiotic activity of totomycin is against Staphylococcus haemolyticus in which growth was inhibited by concentrations of 2 µg/mL. Other gram-positive and gram-negative sensitive to totomycin are inhibited by concentrations from 16 to 31 µg/mL.[2]
Total synthesis
Totomycin has been a successful target in total synthesis since 1989.[3]
References
- R.L. Mann et al., Antibiot. Chemother. 3, 1279 (1953)
- A new antibiotic, Totomycin. Brit. Pat., 758276 (1956)
- N. Chida et al., Chem. Commun. 1989, 436.