Imeglimin
Imeglimin is an experimental drug being developed as an oral anti-diabetic.[1] It is an oxidative phosphorylation blocker that acts to inhibit hepatic gluconeogenesis, increase muscle glucose uptake, and restore normal insulin secretion. It will be the first of a new class of anti-diabetic if it is approved.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
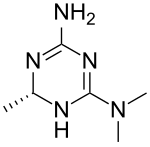
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S)-N6,N6,2-Trimethyl-1,2-dihydro-1,3,5-triazine-4,6-diamine | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C6H13N5 |
| Molar mass | 155.205 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| None | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Vuylsteke, V; Chastain, L. M; Maggu, G. A; Brown, C (2015). "Imeglimin: A Potential New Multi-Target Drug for Type 2 Diabetes". Drugs in R&D. 15 (3): 227–232. doi:10.1007/s40268-015-0099-3. PMC 4561051. PMID 26254210.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.