Acefylline
Acefylline (INN),[1] also known as acetyloxytheophylline, is a stimulant drug of the xanthine chemical class. It acts as an adenosine receptor antagonist. It is combined with diphenhydramine in the pharmaceutical preparation etanautine to help offset diphenhydramine induced drowsiness.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.447 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
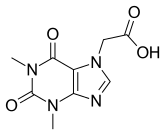
| Formula | C9H10N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 238.203 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
See also
References
- "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names (Rec. INN): List 21" (PDF). World Health Organization. Retrieved 29 December 2016.
- Zuidema J (1978). "Biofarmaceutische en farmacokinetische aspecten van theofylline en acefylline". Thesis (doctoral)--Universiteit van Amsterdam. Archived from the original on 2016-12-30. Retrieved 2012-09-29. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.