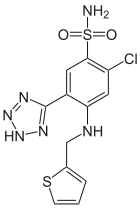
Azosemide
Azosemide is a high-ceiling loop diuretic agent that was brought to market in 1981 by Boehringer Mannheim.[1][2] As of 2015 it was available as a generic in some Asian countries.[3]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.121 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H11ClN6O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 370.83 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Sittig M (1988). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia (PDF). 1. Noyes Publications. p. 122. ISBN 978-0-8155-1144-1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-10-23.
- Bormann D (January 1980). "Diuretics". In Hess HJ (ed.). Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. 15. Academic Press. pp. 100–105 (101). ISBN 978-0-08-058359-4.
- "International listings for azosemide". Drugs.com. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.