Vericiguat
Vericiguat, sold under the brand name Verquvo, is a medication used to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and heart failure.[1][2] It is taken by mouth.[1][2]
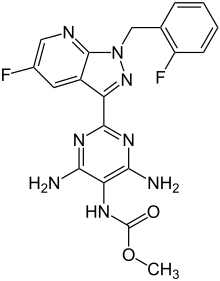 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Verquvo |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Soluble guanylate cyclase activator |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.247.370 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H16F2N8O2 |
| Molar mass | 426.388 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Common side effects include low blood pressure and low red cell count (anemia).[2]
Vericiguat is a soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulator.[1] It was approved for medical use in the United States in January 2021.[2][3]
Medical uses
Vericiguat is indicated to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and heart failure (HF) hospitalization following a hospitalization for heart failure or need for outpatient IV diuretics, in adults with symptomatic chronic HF and ejection fraction less than 45%.[1][2]
Adverse effects
Vericiguat causes harm to the unborn baby and should not be given to pregnant women.[2]
History
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved vericiguat based on evidence from a clinical trial (NCT02861534) which consisted of 5,050 participants aged 23 to 98 years old with worsening heart failure.[2] The trial was conducted at 694 sites in 42 countries in Europe, Asia, North and South America.[2] The trial enrolled participants with symptoms of worsening heart failure.[2] Participants were randomly assigned to receive vericiguat or a placebo pill once a day.[2] Neither the participants nor the health care professionals knew if the participants were given vericiguat or placebo pill until after the trial was complete.[2]
References
- "Verquvo- vericiguat tablet, film coated". DailyMed. Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- "Drug Trials Snapshot: Verquvo". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 8 February 2021. Retrieved 8 February 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Verquvo: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 19 January 2021.
Further reading
- Armstrong PW, Pieske B, Anstrom KJ, Ezekowitz J, Hernandez AF, Butler J, et al. (May 2020). "Vericiguat in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction". N Engl J Med. 382 (20): 1883–1893. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1915928. PMID 32222134.
External links
- "Vericiguat". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Clinical trial number NCT02861534 for "A Study of Vericiguat in Participants With Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF) (MK-1242-001) (VICTORIA)" at ClinicalTrials.gov