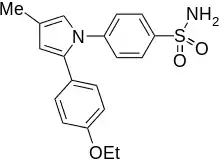
Apricoxib
Apricoxib is an experimental anticancer drug. It is a COX-2 inhibitor which is intended to improve standard therapy response in molecularly defined models of pancreatic cancer.[1] Development was abandoned in 2015 due to poor clinical trial results.[2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H20N2O3S |
| Molar mass | 356.44 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
- Tilmacoxib
- Cimicoxib
- NS-398
- Celecoxib
References
- Kirane A, Toombs JE, Ostapoff K, Carbon JG, Zaknoen S, Braunfeld J, et al. (September 2012). "Apricoxib, a novel inhibitor of COX-2, markedly improves standard therapy response in molecularly defined models of pancreatic cancer". Clinical Cancer Research. 18 (18): 5031–42. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0453. PMC 3777527. PMID 22829202.
- "Apricoxib". Adis Insight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.