Dimethoxanate
Dimethoxanate (trade names Cothera, Cotrane, Atuss, Perlatoss, Tossizid)[1] is a cough suppressant of the phenothiazine class.[2]
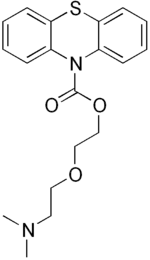 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.838 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H22N2O3S |
| Molar mass | 358.46 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
It may have analgesic, local anesthetic, and central nervous system depressant effects, but it may also produce nausea and vomiting.[3]
Approval for marketing in the US was withdrawn by the FDA in 1975 due to lack of evidence of efficacy.[4]
It binds to the sigma-1 receptor in the brain with an IC50 of 41 nM.[5]
References
- William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia. Elsevier. pp. 1332–3. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3.
- Parish FA (November 1959). "Clinical evaluation of the antitussive, dimethoxanate". Medical Times. 87: 1488–90. PMID 14430450.
- Martín, Alfonso Velasco (2004). "Tratamiento sintomático de la tos y del resfriado común". Farmacología clínica y terapéutica médica. p. 260. ISBN 9788448604271.
- Cough Preparation Containing Dimethoxanate Hydrochloride (PDF). Federal Register (Report). 40. December 18, 1975. 75N–0321.
- Klein M, Musacchio JM (October 10, 1988). "Dextromethorphan binding sites in the guinea pig brain". Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology. 8 (2): 149–156.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.