COVID-19 pandemic in Southeast Asia
The COVID-19 pandemic in Southeast Asia is part of the ongoing worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). It was confirmed to have spread to Southeast Asia on 13 January 2020, when a 61-year-old woman from Wuhan tested positive in Thailand, making it the first country other than China to report a case.[2] The first death occurred on 2 February, involving a 44-year-old Chinese man in the Philippines, also the first outside China.[3]
| COVID-19 pandemic in Southeast Asia | |
|---|---|
| Disease | COVID-19 |
| Virus strain | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Location | Southeast Asia |
| First outbreak | Wuhan, Hubei, China |
| Index case | Suvarnabhumi Airport, Bangkok, Thailand |
| Arrival date | 13 January 2020 (1 year, 2 months, 3 weeks and 6 days) |
| Confirmed cases | 2,858,492[1] |
| Active cases | 285,496[1] |
| Recovered | 2,513,979[1] |
Deaths | 59,017[1] |
| Fatality rate | 2.06% |
Territories | 11 countries[1] |
| Government website | |
| ASEAN COVID-19 Cases | |
By 24 March, all states in the region had announced at least one case. As of 9 April 2021, Indonesia has the highest number of cases and deaths, ahead of the Philippines in both aspects. No deaths have been reported in East Timor and Laos. Both of them, along with Brunei, are the three least affected countries in Asia (excluding the special administrative region of Macau).
Background
On 12 January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed that a novel coronavirus was the cause of a respiratory illness in a cluster of people in Wuhan, Hubei, China, which was reported to the WHO on 31 December 2019.[4][5]
The case fatality ratio for COVID-19 has been much lower than SARS of 2003,[6][7] but the transmission has been significantly greater, with a significant total death toll.[8][6]
Timeline
Southeast Asia was among the first regions to be affected by the pandemic. Thailand, the Philippines, Singapore, Cambodia, Vietnam, and Malaysia reported the index cases in January 2020 and since then their cases were increasing. Indonesia, a country with around 270 million population, reported its first cases in March which was relatively late compared to its neighbouring countries, but now being the worst-hit nation in the region.
January–June
- 13 January: First case in Thailand.
- 23 January
- First case in Singapore.
- First cases in Vietnam.
- 24 January: First cases in Malaysia.
- 27 January: First case in Cambodia.
- 28 January: Thailand passed 10 cases.
- 29 January: Singapore passed 10 cases.
- 30 January: First case in the Philippines.
- 4 February
- Malaysia passed 10 cases.
- Vietnam passed 10 cases.
- 5 February: First death in the Philippines.
- 15 February: The Philippines passed 10 deaths.
- 29 February: Singapore passed 100 cases.
- 1 March: First death in Thailand.
- 2 March: First cases in Indonesia.
- 8 March: The Philippines passed 10 cases.
- 9 March
- First case in Brunei.
- Indonesia passed 10 cases.
- Malaysia passed 100 cases.
- 11 March
- First death in Indonesia.
- Brunei passed 10 cases.
- 14 March: The Philippines passed 100 cases.
- 15 March
- Cambodia passed 10 cases.
- Indonesia passed 100 cases.
- Thailand passed 100 cases.
- 17 March: First deaths in Malaysia.
- 18 March: Indonesia passed 10 deaths.
- 20 March: Malaysia passed 1,000 cases.
- 21 March
- First deaths in Singapore.
- First case in East Timor.
- 22 March
- Malaysia passed 10 deaths.
- Vietnam passed 100 cases.
- 23 March: First cases in Myanmar.
- 24 March
- First cases in Laos.
- Brunei passed 100 cases.
- 26 March: Thailand passed 1,000 cases.
- 27 March: Indonesia passed 1,000 cases.
- 28 March
- First death in Brunei.
- Indonesia passed 100 deaths.
- Cambodia passed 100 cases.
- The Philippines passed 1,000 cases.
- 29 March: Myanmar passed 10 cases.
- 31 March
- First death in Myanmar.
- Thailand passed 10 deaths.
- 1 April
- Laos passed 10 cases.
- Singapore passed 1,000 cases.
- 2 April: The Philippines passed 100 deaths.
- 14 April: Singapore passed 10 deaths.
- 16 April: East Timor passed 10 cases.
- 18 April: Myanmar passed 100 cases.
- 22 April: Singapore passed 10,000 cases.
- 29 April: Malaysia passed 100 deaths.
- 30 April: Indonesia passed 10,000 cases.
- 6 May: The Philippines passed 10,000 cases.
- 12 May: Indonesia passed 1,000 deaths.
- 7 June: The Philippines passed 1,000 deaths.
July–December
- 27 July: Indonesia passed 100,000 cases.
- 31 July: First deaths in Vietnam.
- 2 August: The Philippines passed 100,000 cases.
- 6 August: Vietnam passed 10 deaths.
- 20 August: Vietnam passed 1,000 cases.
- 3 September: Myanmar passed 1,000 cases.
- 8 September: Myanmar passed 10 deaths.
- 16 September: Malaysia passed 10,000 cases.
- 22 September: Myanmar passed 100 deaths.
- 24 September: Indonesia passed 10,000 deaths.
- 27 September: Myanmar passed 10,000 cases.
- 22 October: Myanmar passed 1,000 deaths.
- 7 December: Myanmar passed 100,000 cases.
- 24 December: Malaysia passed 100,000 cases.
January–June
- 9 January: Thailand passed 10,000 cases.
- 20 January: The Philippines passed 10,000 deaths.
- 26 January: Indonesia passed 1,000,000 cases.
- 11 February: East Timor passed 100 cases.
- 17 February: Malaysia passed 1,000 deaths.
- 8 March: Cambodia passed 1,000 cases.
- 11 March: First death in Cambodia.
- 28 March: Cambodia passed 10 deaths.
Confirmed cases
Brunei
.svg.png.webp)
Brunei confirmed its first case on 9 March 2020 in Tutong, involving a 53-year-old man who had returned from Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia on 3 March.[9] It has spread to all districts of Brunei, except in the exclave of Temburong.
Cambodia
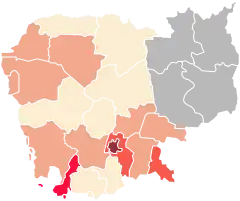
On 27 January 2020, Cambodia announced its first case in Sihanoukville. It involved a 60-year-old Chinese man who had travel history to Wuhan with his family.[10]
East Timor
East Timor confirmed its first COVID-19 case on 21 March 2020. It was an imported case and its origin is unknown.[11]
Indonesia
.svg.png.webp)
Indonesia reported its first cases on 2 March 2020, after a dance instructor and her mother were tested positive for the virus. Both were in contact with a Japanese national who was later tested positive in Malaysia.[12] By 9 April, it had spread to all 34 provinces in the country. Jakarta, West Java, and Central Java are the worst-hit provinces.
Laos
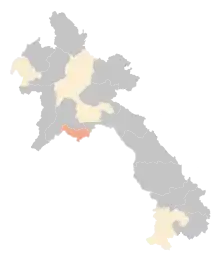
Laos confirmed its first cases on 24 March 2020, becoming the last country in Southeast Asia to report COVID-19 cases.[13]
Malaysia
.svg.png.webp)
Malaysia announced its first cases on 25 January 2020. It started when eight Chinese nationals were quarantined at a hotel in Johor Bahru on 24 January after coming into contact with an infected person in neighbouring Singapore.[14] Despite early reports of them tested negative for the virus,[15] three of them were confirmed to be infected on 25 January and subsequently quarantined at the Sungai Buloh Hospital in Selangor.
Myanmar
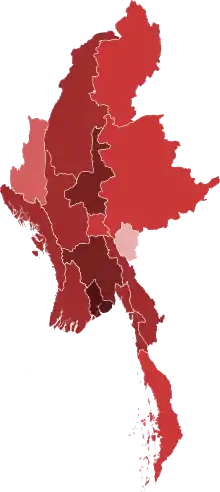
The pandemic reached Myanmar on 23 March 2020. Its first two cases involved a 36-year-old man travelling back from the United States and a 26-year-old man returning from Great Britain. Both were Myanmarese nationals and had tested positive.[16]
Philippines
.svg.png.webp)
On 30 January 2020, the Philippines confirmed its first case in Metro Manila. It involved a 38-year-old Chinese woman who was confined in San Lazaro Hospital in Manila. The second case was confirmed on 2 February, involving a 44-year-old Chinese man who died a day earlier, which was also the first confirmed death from the disease outside mainland China.
Singapore
Singapore reported its first case on 23 January 2020, involving a 66-year-old Chinese man who flew in from Guangzhou with his family.[17]
Thailand
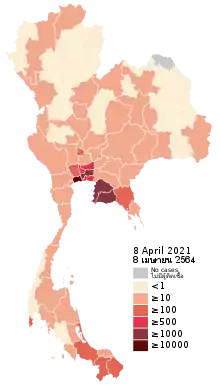
Thailand became the first country outside China to report a case. Its first case was on 13 January 2020, involving a 61-year-old Chinese woman who was a resident of Wuhan. She flew with her family to Suvarnabhumi Airport in Bangkok on 8 January where she was detected using a thermal surveillance and then hospitalised. A few days later she was tested positive for the virus.
Vietnam
On 23 January 2020, it was confirmed that the pandemic had spread to Vietnam, when a 66-year-old Chinese man travelling from epicenter Wuhan to Hanoi to visit his son tested positive. His son contracted the virus from his father when they met in Nha Trang.[18]
Statistics
| Countries or territories | Index case(s) | Cases | Recoveries | Deaths | Active | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date[lower-alpha 1] | Location | 2,858,492 | 2,513,979 | 59,017 | 285,496 | |
| 9 March | Tutong | 213 | 195 | 3 | 15 | |
| 27 January | Sihanoukville | 2,477 | 1,240 | 14 | 1,223 | |
| 21 March | Unknown | 643 | 192 | 0 | 451 | |
| 2 March | Kemang | 1,517,854 | 1,355,578 | 41,054 | 121,222 | |
| 24 March | Vientiane | 49 | 45 | 0 | 4 | |
| 25 January | Johor Bahru | 346,678 | 331,001 | 1,278 | 14,399 | |
| 23 March | Tedim | 142,466 | 131,802 | 3,206 | 7,458 | |
| 30 January | Manila | 756,199 | 603,948 | 13,303 | 138,948 | |
| 23 January | Sentosa | 60,407 | 60,161 | 30 | 216 | |
| 13 January | Bangkok | 28,889 | 27,548 | 94 | 1,247 | |
| 23 January | Ho Chi Minh City | 2,617 | 2,359 | 35 | 223 | |
Notes
- All occurred in 2020.
References
- "COVID-19 Update". 1 April 2021.
- Cheung, Elizabeth (13 January 2020). "Thailand confirms first case of Wuhan virus outside China". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 13 January 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- Ramzy, Austin; May, Tiffany (2 February 2020). "Philippines Reports First Coronavirus Death Outside China". The New York Times. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- Elsevier. "Novel Coronavirus Information Center". Elsevier Connect. Archived from the original on 17 March 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- Reynolds, Matt (4 March 2020). "What is coronavirus and how close is it to becoming a pandemic?". Wired UK. ISSN 1357-0978. Archived from the original on 17 March 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- "Crunching the numbers for coronavirus". Imperial News. Archived from the original on 15 March 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- "High consequence infectious diseases (HCID); Guidance and information about high consequence infectious diseases and their management in England". GOV.UK. Archived from the original on 3 March 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- "World Federation Of Societies of Anaesthesiologists – Coronavirus". www.wfsahq.org. Archived from the original on 12 March 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- "Latest news – Detection of the First Case of COVID-19 Infection". Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Cambodia confirms first case of coronavirus: Health minister". CNA Asia. 27 January 2020. Archived from the original on 27 January 2020. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "East Timor Confirms First Case of Coronavirus: Health Ministry". The New York Times. Reuters. 21 March 2020. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Indonesia confirms first cases of coronavirus". Bangkok Post. Reuters. 2 March 2020. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Laos Confirms First Covid-19 Cases". 24 March 2020. Archived from the original on 24 March 2020. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- Loh, Ivan (24 January 2020). "Wuhan virus: Eight in isolation in JB after coming into contact with Singapore victim". The Star. Archived from the original on 17 February 2020. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Eight Chinese tourists show no coronavirus symptoms in Johor Baru". The Malay Mail. Bernama. 24 January 2020. Archived from the original on 17 February 2020. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- hermesauto (24 March 2020). "Myanmar confirms first two coronavirus cases". The Straits Times. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- Abdullah, Zhaki; Salamat, Hidayah (23 January 2020). "Singapore confirms first case of Wuhan virus". CNA. Archived from the original on 13 June 2020. Retrieved 16 July 2020.
- Hai ca dương tính nCoV đang điều trị tại BV Chợ Rẫy. Ministry of Health (Vietnam). 30 June 2020.